+86-(0755) 2331 8242
Info@longrunled.com
Outdoor LED display is not only an information dissemination medium, but also a unique symbol showing the image of the city. Is the operating temperature of your LED display also soaring when the sun is exposed to the sun outdoors?
Why does the display need to dissipate heat?
The temperature of the display screen is closely related to its performance. Excessive temperature directly affects the working efficiency of the screen:
1. Wavelength drift: Wavelength drift affects the color correction of the display screen. When the temperature of the LED display screen changes greatly, the wavelength drift becomes larger.
2. Reduce the luminous efficiency of the LED display.
3. High junction temperature leads to shortened LED life.
4. Aggravate the light decay of LED display.
5. The internal circuit uses too many heat dissipation components, resulting in increased costs.
Display cooling solution
So, how can outdoor LED displays calmly cope with high temperature weather?
1. Adopt the principle of air fluid mechanics and use the shape of the lamp shell to create convection air.
2. Use a thermally conductive shell for heat dissipation, and fill the shell with thermally conductive materials during injection molding to increase the thermal conductivity and heat dissipation capabilities of the shell.
3. Use aluminum heat dissipation fins as part of the housing to increase the heat dissipation area.
4. The lamp shell is treated with surface radiation heat dissipation, which can take part of the heat away from the surface of the lamp shell by radiation.
5. Use Longrun outdoor shared cooling screen to eliminate the worry of heat dissipation and improve the work efficiency of the display screen!
Longrun C series of outdoor common cathode cold screens use common cathode lamp beads and are powered separately, which solves the problem of difficult heat dissipation of outdoor displays from the source.
We tested the outdoor common cathode cold screen (hereinafter referred to as "cold screen") and the outdoor conventional display screen (hereinafter referred to as "common anode display") with the same size and the same point spacing.
Through white balance test comparison and temperature test comparison, we used data Explain where the "cold" is in the common cold screen.
Test objects: PH3.8/PH4 common cathode cold screen and PH3.8/PH4 common anode display
Test environment: outdoor
Ambient temperature:25°C
Wind speed: breeze
Under the test brightness of 3200cd and white balance of 255, the temperature change was tested for 10 minutes;
Play the video for 10 minutes to test the temperature change.
Note: The test sample uses 1919-NB pure black lamp beads with a high contrast ratio of 10000:1, which is equivalent to the brightness of an ordinary white lamp of about 7000cd.
Common cathode/common anode display temperature test:

Temperature data after 5 minutes:

The temperature of the common cold screen is 39℃, and the temperature of the common positive screen is 46℃
Temperature data after 10 minutes:
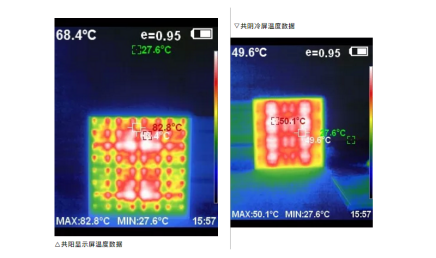
At this time, the average temperature difference between the common anode display screen and the common cathode cold screen is about 18°C. From the image captured by the infrared thermal imaging camera screen, it can be seen that the high temperature area on the surface of the common anode display screen is distributed in a point-like manner;while the surface temperature distribution of the common cathode cold screen is relatively average.
What is the difference between outdoor common cathode cold screen and common anode display?
Common anode display screen:
Conventional LED displays are generally powered by a common anode. The voltage requirements of red, green and blue lamp beads are different (the voltage requirement of red lamp beads is about 2.5V, and the voltage requirement of blue and green lamp beads is about 3.8V). Common anode display screens are usually given a voltage higher than 3.8V, while the current The input flow from the PCB board to the lamp beads not only increases the forward voltage drop of the circuit, but also causes excessive power loss. Therefore, as the working time of the common anode LED display gradually increases, the lamp beads will become overheated and the temperature distribution will be uneven, which will directly cause the appearance of color blocks and the visual effect of inconsistent colors on the entire screen.
Longrun C series outdoor common shade cooling screen:
The common cathode cooling screen uses separate power supplies for R and GB, that is, the voltage and current are accurately distributed to the red, green and blue lamp beads. The current passes through the lamp beads and then to the negative electrode of the IC. The forward voltage is reduced and the internal resistance is small. The separate power supply scheme effectively reduces power consumption and greatly reduces the heat generated during the operation of the display.
The common cathode cooling screen adopts the ICN2069+2019 solution. The IC has a PWM pulse width modulation function and is active at low level. Truly realize LED display screen with low voltage drop, low temperature rise, low power consumption, green energy saving and environmental protection.
The common cathode cold screen adopts the customized version of 1919 common cathode lamp beads jointly developed by Longrun & Chipone Electronics. 1919 common cathode lamp beads have the advantages of high brightness, high contrast, and consistent lamp bead ink color. You can choose 1919NW white lamp/1919NB black lamp according to the actual application scenario.